Core Concepts and Key Technologies
A Cylindrical capacitor is typically designed for power factor correction or Reactive Power Compensation in AC networks. Its cylindrical geometry allows uniform electric field distribution and efficient heat dissipation, which are critical for stable operation under continuous electrical stress.
Key technical concepts include:
● Reactive power compensation: By supplying leading reactive power, the Capacitor offsets the lagging reactive power generated by inductive loads such as motors and transformers.
● Dielectric system stability: The dielectric material must withstand repeated charge-discharge cycles while maintaining low loss and stable capacitance.
● Thermal management: Heat generated by dielectric losses and current flow must be dissipated efficiently to prevent premature aging.
● Self-healing behavior: Modern metallized film technologies allow localized dielectric breakdowns to self-clear without catastrophic failure.
These principles directly influence how cylindrical capacitors are designed, manufactured, and applied in industrial systems.
Product Structure, Materials, and Manufacturing Process
From an engineering standpoint, the performance of a cylindrical capacitor is determined by the integration of its structural, material, and process design.
Structural Design
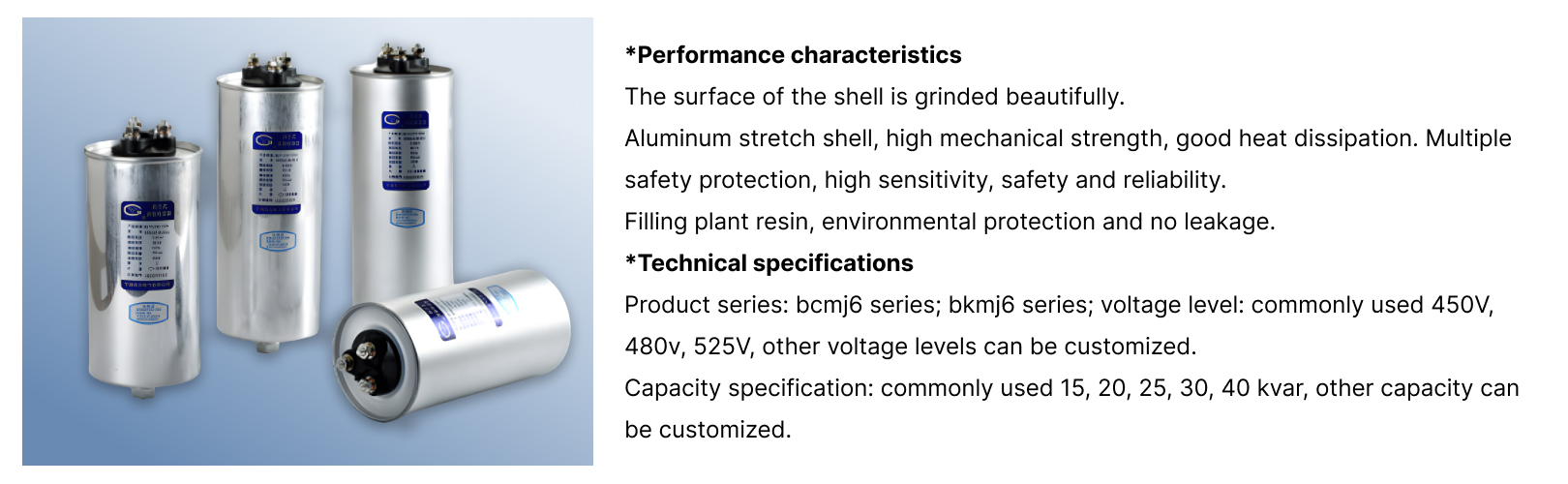
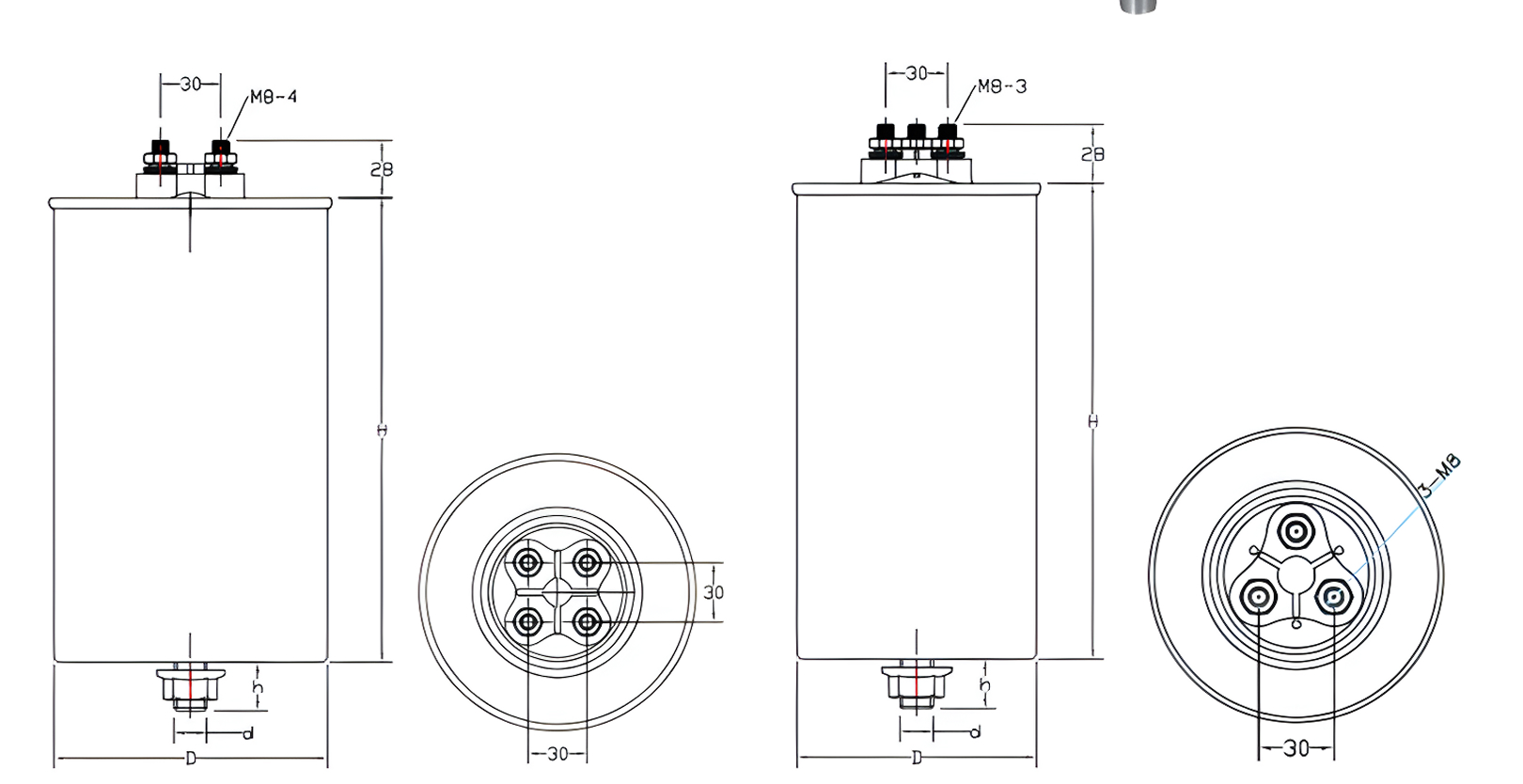
The cylindrical shell is commonly manufactured from aluminum due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio and thermal conductivity. A stretched aluminum shell provides high mechanical strength, enabling the capacitor to withstand internal pressure variations and external mechanical stress during installation or operation.
The smooth, finely ground surface of the shell is not merely aesthetic; it reduces localized stress points, improves corrosion resistance, and enhances heat transfer to the surrounding environment.
Internal Construction
Inside the shell, metallized film elements are wound with controlled tension to ensure consistent electrical characteristics. The winding geometry directly affects inductance, loss factor, and thermal behavior. Precision winding equipment and strict process control are therefore essential.
After assembly, the internal space is filled with plant-based resin. This resin serves multiple functions:
● It provides electrical insulation.
● It improves heat transfer from the winding to the shell.
● It eliminates air gaps, reducing the risk of partial discharge.
● It prevents leakage and aligns with environmental compliance requirements.
Safety Protection Design
Modern cylindrical capacitors integrate multiple safety mechanisms, such as overpressure disconnection devices and highly sensitive internal protection structures. These features ensure that, in abnormal conditions, the capacitor fails in a controlled and non-hazardous manner, maintaining system safety and reliability.
Key Factors Affecting Quality and Performance
Several variables determine whether a cylindrical capacitor will deliver consistent performance over its intended service life:
1. Voltage Margin: Operating a capacitor close to its rated voltage accelerates dielectric aging. Designs commonly account for voltage derating to enhance longevity.
2. Thermal Environment: Ambient temperature and ventilation conditions significantly influence service life. Effective heat dissipation through the aluminum shell is critical.
3. Capacitance Stability: High-quality dielectric materials ensure minimal capacitance drift over time.
4. Manufacturing Consistency: Variations in winding tension, resin filling, or sealing processes can lead to uneven electrical stress.
5. Protection Sensitivity: Reliable safety mechanisms prevent secondary damage to connected equipment in the event of internal faults.
Understanding these factors helps engineers select components that match both electrical requirements and environmental constraints.
Supplier Selection and Supply Chain Considerations
For OEMs and system integrators, selecting a cylindrical capacitor supplier involves more than comparing nominal specifications. Key evaluation criteria include:
● Process traceability: Documented manufacturing processes and quality control systems.
● Compliance: Alignment with IEC and other relevant international standards.
● Customization capability: Ability to support different voltage levels (such as 450 V, 480 V, or 525 V) and capacitance ratings without compromising consistency.
● Long-term availability: Stable supply chains that support multi-year projects and maintenance cycles.
● Technical support: Engineering expertise to assist with application-specific challenges.
A transparent supply chain reduces lifecycle risk and supports predictable system performance.
Common Industry Challenges and Pain Points
Despite their mature design, cylindrical capacitors are often misapplied. Common issues include:
● Underrated voltage selection, leading to accelerated failure.
● Inadequate thermal consideration in enclosed panels.
● Ignoring harmonic conditions, which can increase dielectric stress.
● Assuming all capacitors are interchangeable, without considering internal design differences.
Addressing these challenges requires close collaboration between design engineers, procurement teams, and component suppliers.
Application Scenarios and Use Cases
Cylindrical capacitors are widely used across industries:
● Manufacturing plants: Power factor correction in motor-driven equipment.
● HVAC systems: Stabilizing voltage and reducing energy losses in large compressors.
● Elevators and lifts: Improving efficiency and reducing grid impact during peak load cycles.
● Renewable energy systems: Supporting reactive power balance in inverter-based installations.
● Electrical panels and switchgear: Compact form factor enables flexible installation in space-constrained environments.
In each case, the cylindrical form simplifies integration while delivering consistent electrical performance.
Current Trends and Future Development
The evolution of the cylindrical capacitor reflects broader trends in electrical engineering:
● Higher energy density: Advances in dielectric films allow more capacitance in smaller volumes.
● Improved sustainability: Environmentally friendly resins and recyclable aluminum housings are becoming standard.
● Enhanced monitoring: Integration with smart power systems enables predictive maintenance.
● Customization over standardization: Tailored voltage and capacity configurations are increasingly preferred.
As power systems become more complex and efficiency-driven, cylindrical capacitors will continue to evolve as engineered components rather than passive accessories.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a cylindrical capacitor differ from other capacitor shapes?
Its geometry offers better mechanical strength and thermal dissipation compared to flat or box-type designs.What determines service life?
Operating voltage, temperature, dielectric quality, and internal protection design are the primary factors.Can cylindrical capacitors be customized?
Yes, voltage levels and capacitance values are often adjustable to meet specific system requirements.Are they suitable for continuous operation?
When correctly rated and installed, they are designed for long-term continuous duty in industrial environments.

 English
English
 Español
Español
 Portugues
Portugues
 Pусский
Pусский
 Français
Français
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 日本語
日本語
 한국어
한국어
 العربية
العربية
 Italiano
Italiano
 Nederlands
Nederlands
 Svenska
Svenska
 Polski
Polski
 Türk dili
Türk dili
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी
 Indonesia
Indonesia
 Melayu
Melayu
 dansk
dansk
 Magyar
Magyar
 қазақ
қазақ
 עִברִית
עִברִית
 čeština
čeština
 українська
українська
 беларускі
беларускі
 Filipino
Filipino
 Suomalainen
Suomalainen
 اردو
اردو
 հայերեն
հայերեն
 български
български
 Hrvatski
Hrvatski
 galego
galego
 नेपाल
नेपाल
 euskara
euskara
 Shqipëria
Shqipëria
 Malagasy
Malagasy
 Башҡорт
Башҡорт
 Türkmenler
Türkmenler
 Ilocano
Ilocano
 Нохчийн
Нохчийн














 হোয়াটসঅ্যাপ
হোয়াটসঅ্যাপ টেলিফোন
টেলিফোন